In the competitive landscape of the auto parts industry, understanding the key players is crucial for business owners looking to optimize their supply chain. 湛江德利车辆部件有限公司 stands out for its specialization in aluminum and magnesium alloy components, leveraging advanced production techniques to meet diverse automotive needs. Through its IATF16949:2016 certification, the company maintains high quality standards critical for automotive performance and safety. Additionally, this article explores the growth of its subsidiary, 广州德利汽车零部件有限公司, and the market influence of Chinese manufacturers like 湛江德利. Each chapter builds on the previous insights, providing a comprehensive overview that can inform your business decisions in the automotive parts sector.
Tracing the Roots Behind De Leon Auto Parts: A Close Look at Zhanjiang De Li Vehicle Components and Its Role in the Global Auto Parts Network

Tracing the roots behind a name tied to global auto parts can be a complex exercise in parsing corporate lineage, naming conventions, and the realities of supply chains. In the context of the broader topic of De Leon Auto Parts, this chapter centers on a Chinese manufacturer that often appears in discussions about quality and reliability within the auto parts ecosystem: Lingzhi De Li Vehicle Components Co., Ltd., based in Zhanjiang. While there is no verified independent entity known as De Leon Auto Parts in the core records, Lingzhi De Li serves as a compelling case study. It illustrates how similarly named firms, historical mergers, and cross-border collaborations shape what buyers encounter when they source components for modern vehicles. The company discussed here has built a substantial footprint in the automotive parts industry through a carefully orchestrated evolution from its origins as a carburetor manufacturer to a broader supplier of engine system components for passenger cars and light commercial vehicles. In this sense, the chapter offers a grounded framework for how a supplier under a Chinese corporate umbrella gains access to both national automaker networks and international markets, a framework that underpins many imports into regions where De Leon Auto Parts might be considered by buyers seeking reliability and scale.
The company began its life in November 1992 as a Sino-foreign joint venture situated in Zhanjiang, Guangdong, a city with growing port access that would later become advantageous for international trade. The founding consortium included a major national automaker, a multinational agri-industrial participant, and a regional industrial group. The early focus centered on automotive components, particularly those required by two- and three-wheel markets before the business expanded its scope. A pivotal shift occurred in 2011 when the business was acquired by a subsidiary of a large state-owned automotive conglomerate, cementing its integration into a broader corporate ecosystem. The acquisition did more than change ownership; it signaled a strategic commitment to diversification beyond its original product lines. By 2014 the entity officially rebranded to better reflect its expanded scope, signaling its transition from motorcycle-specific components to an emphasis on automotive solutions for modern cars and light commercial vehicles. This evolution underpins the company’s current emphasis on engine system components and related subsystems that are essential for contemporary vehicle performance and reliability.
The core business narrative centers on research, development, and manufacturing capabilities that support both domestic automakers and international customers. The company now concentrates on a portfolio that enables precise engine management and running-system integrations, which are critical for achieving smooth combustion, efficient thermal regulation, and robust reliability in everyday driving. The commercial footprint includes major domestic brands that are part of the broader Dongfeng Motor Group ecosystem, under which the supplier operates as a trusted partner. The presence of overseas demand, particularly in North America, underscores the company’s export orientation. In addition to serving China’s rapidly expanding vehicle market, Lingzhi De Li has built export channels that align with buyers seeking high-quality, technologically capable components. This dual domestic and international orientation reveals the strategic posture of a modern auto parts manufacturer that must navigate complex procurement systems and stringent quality expectations across multiple markets.
A key element in the company’s credibility is its commitment to quality management and environmental, health, and safety standards. The business has embraced global and regional quality frameworks that help ensure consistent performance across production lines and product families. Certifications such as ISO/TS 16949 and related environmental and safety standards signal a mature quality culture. Beyond process certification, the company has also built a substantial intellectual property portfolio, reflecting a strategy that values innovation as a driver of differentiation. The portfolio includes a substantial number of patents along with several registered trademarks, demonstrating a formalized approach to protecting and leveraging its know-how and product designs. This emphasis on IP and technology centers underscores the importance of innovation in the auto parts sector, where downstream value is increasingly tied to the precision, efficiency, and durability of components rather than pure volume manufacture.
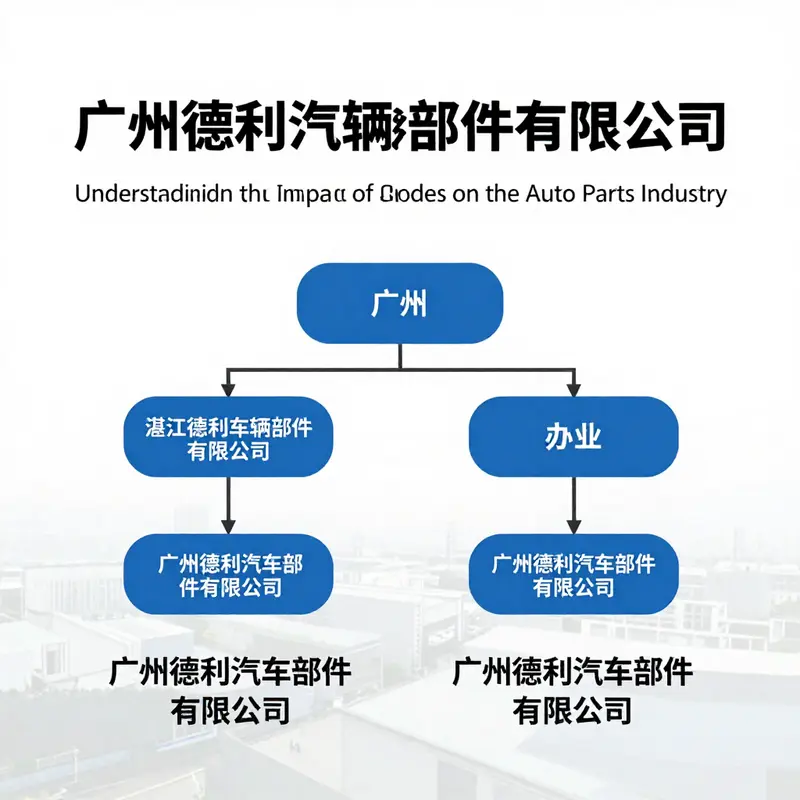
From a manufacturing perspective, the enterprise operates across multiple sites that form a coherent network supporting scale and resilience. The headquarters in Zhanjiang anchors primary operations, complemented by a significant presence at the Dongfeng non-ferrous castings facility and a dedicated subsidiary in Guangzhou. The distributed footprint enables flexible production planning, closer proximity to key suppliers, and more efficient logistics for both domestic distribution and international shipping. The scale of employment—ranging from roughly one thousand to several thousand workers depending on period and report—reflects the labor-intensive nature of precision casting, assembly, and finishing activities common to modern auto parts production. In 2024 the company reported revenues that place it among notable regional players in the automotive components landscape, signaling robust demand and healthy output across its product families. Taken together, these structural elements illustrate how a regional supplier can grow into a segment leader by stitching together technology, manufacturing discipline, and market access in a strategically important sector.
The industry position of this Guangdong-based company is not accidental. Its integration within the supply networks of a major automaker group anchors it as a reliability-focused partner capable of meeting the demanding timetables and quality specifications of large-scale vehicle programs. This integration is not merely about supplying parts; it is about contributing to a synchronized procurement architecture in which procurement systems, supplier development programs, and continuous improvement initiatives are harmonized with the automaker’s own manufacturing cadence. The Zhanjiang location, with its access to port facilities and nearby logistics corridors, further enhances export readiness, enabling smoother displacement of finished components toward North American and other overseas markets. The company’s technology center designation at the provincial level signals a structured commitment to ongoing process improvement, product refinement, and the development of advanced manufacturing capabilities. In a sector where even small efficiency gains can translate into meaningful competitive advantages, such a positioning matters for automakers and for downstream distributors who require consistent quality and reliable delivery.
A closer look at the corporate structure reveals a disciplined approach to governance, with two wholly owned subsidiaries and a network of manufacturing sites organized to optimize both cost and performance. The Guangzhou subsidiary extends the group’s geographic reach and supports regional engineering and supply chain activities, creating a bridge between the headquarters and the larger southern manufacturing cluster. This arrangement is not just about assets on the balance sheet; it reflects a deliberate strategy to cultivate regional know-how, align with localized talent pools, and leverage proximity to customers and material suppliers in the Pearl River Delta–Guangzhou area. The overarching narrative of the company thus reads as a model of strategic consolidation: a core national player expanding through targeted acquisitions, a multi-site footprint that increases operational resilience, and a robust IP portfolio that preserves a path toward future capabilities.
For readers mapping the terrain of De Leon Auto Parts, this case study offers a practical reminder that the global auto parts market is a mosaic of branding, naming conventions, and corporate structures rather than a single monolithic entity. The Lingzhi De Li example demonstrates how a regional supplier with a strong technical core can become a key node in a multinational supply chain while maintaining a local identity and a regional technology footprint. It also highlights why international buyers must perform due diligence that goes beyond brand recognition, assessing quality certifications, IP holdings, and the sustainability of production networks. In that sense, the broader article’s theme—understanding the landscape of auto parts sourcing—gains depth from examining how a single Chinese supplier evolved to meet global standards. The story invites readers to consider how a brand’s perceived identity may lag behind the actual capabilities embedded in its production system, its technology base, and its strategic alliances.
As the narrative unfolds across chapters, this chapter should serve as a reminder of the complexity and richness of the auto parts ecosystem and of the careful evaluation required when aligning with suppliers who share a linguistic or nominal shorthand with a potential buyer’s brand. It is not a critique of any single company but rather a precisa map of how modern auto parts businesses operate, grow, and connect with the far-flung markets that define today’s global automotive industry. With that understanding, readers can better navigate the confluence of naming, corporate lineage, and practical capability that underpins the broader topic of De Leon Auto Parts and its place in an ever-evolving supply chain landscape.
Precision Casting and Lightweight Strategies: How 湛江德利 Shapes Aluminum and Magnesium Components for Modern Vehicles

Precision casting and lightweight strategies drive the manufacturing philosophy at 湛江德利车辆部件有限公司. Their approach centers on converting advanced alloy metallurgy into reliable, repeatable components for both internal combustion and electrified powertrains. This chapter examines the manufacturing techniques and process architecture that let the company produce complex die-cast parts at scale, while controlling quality, energy use, and material performance.
The backbone of production is high-precision die-casting. 湛江德利 upgraded its operations with a technical transformation project that introduced intelligent die-casting machines. These machines provide closed-loop control of injection velocity, molten metal temperature, and plunger position. Accurate control reduces common defects such as gas porosity and cold shuts. The integration of robotic handling further shortens cycle times and minimizes human variability, improving surface finish and dimensional stability for parts like engine casings and structural housings.
Die design and gating strategy are critical for thin-walled, high-integrity parts. 湛江德利 applies robust simulation and CAE-driven mold design to predict flow patterns, solidification paths, and areas prone to shrinkage. Optimized gates and runners ensure stable flow and minimize rework. For aluminum-silicon alloys, controlled solidification reduces eutectic segregation. For magnesium alloys, where flammability and rapid heat transfer complicate casting, the company implements strict process windows and protective atmospheres to ensure safety and metallurgical soundness.
Melting and metal treatment form the next pillar. A centralized energy-saving melting furnace enhances thermal efficiency and reduces alloy contamination. Consistent melt treatment—degassing, fluxing, and adjusting silicon or alloying element levels—delivers repeatable chemistry. Vacuum-assisted systems reduce dissolved hydrogen in the melt, lowering the incidence of porosity. For magnesium, fluxes and cover gases minimize oxidation. Automated alloy dosing and inline spectrometers keep compositions within tight tolerances, essential for downstream heat treatment responsiveness and mechanical performance.
Post-casting processing merges automated CNC machining with robotic cell integration. 湛江德利 equipped its plant with over a hundred high-precision machining centers. These centers remove gates, trim features, and machine critical surfaces to final tolerances. The company applies multi-axis machining strategies to reduce setups and preserve part integrity. Robotic integrated processing cells handle part transfer, deburring, and inspection automatically, maintaining throughput while reducing manual handling and potential damage.
Surface quality and corrosion protection are treated as inherent design considerations. For aluminum parts, surface machining is followed by controlled anodizing or conversion coatings depending on application. Magnesium components receive thin, protective conversion coatings to mitigate galvanic concerns when paired with dissimilar metals. Automated cleaning systems prior to coating remove residues and ensure adhesion. For external housings and consumer-visible components, surface finishing processes include shot peening and micro-blasting to improve fatigue life and appearance.
Heat treatment and stress relief are applied selectively. While many die-cast components rely on the as-cast microstructure, critical load-bearing features benefit from solution and aging treatments. For aluminum alloys, T6 or T7 tempering can increase strength at the cost of some ductility. Careful selection of heat treatment schedules ensures that dimensional stability and mechanical requirements are met without compromising internal clearances or mating surfaces.
Quality assurance combines traditional inspection with advanced non-destructive techniques. Dimensional control uses coordinate measuring machines and in-process probing to verify features against CAD models. X-ray and CT scanning detect internal voids and inclusions. Mechanical tests, including tensile, hardness, and fatigue sampling, ensure that batches meet specifications. Traceability is embedded across the value chain through barcode and RFID systems, linking each part to its melt batch, process parameters, and inspection records—an essential requirement under modern automotive quality standards.
Sustainability and energy performance are tangible outcomes of process choices. The new centralized melting furnace and energy targets cap annual consumption at a measured standard-coal equivalent. Recycling scrap and remelting allowances are optimized to reduce virgin alloy demand. Process automation reduces scrap rates through consistent cycle control. These measures allow high-volume output—tens of thousands of tons of aluminum equivalents—while limiting environmental impact.
Material selection reflects market shifts. The company focuses on aluminum-silicon and magnesium-aluminum families, balancing strength, weight, and cost. Aluminum offers good castability and corrosion resistance. Magnesium delivers greater density savings but requires careful handling and protective measures. For electric motor components, lightweight housings and end-covers improve vehicle efficiency. 湛江德利 has filed patents for manufacturing processes targeted at electric motor rear covers and press rings, signaling a strategic emphasis on EV components where lightweight alloys play a key role.
Process monitoring and Industry 4.0 concepts support continuous improvement. Sensors collect temperature, pressure, and cycle data, feeding analytics that detect drift and alert operators. Predictive maintenance on critical presses and furnaces reduces downtime. Die life is extended through optimized cooling channels and surface coatings that resist thermal fatigue. Simulation-driven die updates shorten revision cycles and improve first-pass yield.
Meeting scale requires careful logistics and supply chain alignment. Producing thousands to tens of thousands of tons annually demands steady alloy supply and consistent scrap return streams. 湛江德利 coordinates with upstream suppliers for cast alloys and downstream assembly partners for just-in-time deliveries. Kitting, labeling, and sequencing align with assembly line demands to reduce inventory and lead time.
Manufacturing for high-volume automotive applications places heavy emphasis on repeatability and process control. 湛江德利’s combination of intelligent die-casting, extensive CNC capabilities, robotic processing, and energy-efficient melting furnaces creates a production environment capable of delivering complex castings with stable quality. Practical examples of downstream use of such castings include engine blocks and housings, comparable in function to a billet engine block reference found in service and aftermarket discussion of engine components (see 4B11T billet block).
Taken together, these techniques create a modern foundry and machining operation. 湛江德利 leverages metallurgy, automation, and rigorous quality systems to supply components that meet the demands of both traditional powertrains and the emerging electric vehicle market. For a detailed description of the project’s approval and technical scope, refer to the Guangdong Provincial Development and Reform Commission approval document: https://www.gdrc.gov.cn/xxgk/zwgk/gzdt/202303/t20230324_7239834.html
Quality Assurance in Automotive Parts: IATF16949:2016 Certification and the Making of Trusted Components at Zhanjiang Deli Vehicle Parts Co., Ltd.

Quality assurance in automotive parts is more than a checklist of tests; it is a disciplined mindset that shapes every link in the supply chain. For a company operating in southern China, where metal comes from foundries and precision is forged in tooling and process, achieving IATF16949:2016 certification marks a decisive shift from reactive inspection to proactive control. The standard itself sits atop ISO 9001:2015, but its real power lies in the automotive industry’s insistence on a process-based approach and risk management that permeates design, development, manufacturing, and post-sale service. When applied to a company like Zhanjiang Deli Vehicle Parts Co., Ltd.—a producer known for aluminum and magnesium die-cast parts and fuel-system components—the certification becomes more than a symbol; it becomes a structural feature of the business model. In practice, it requires a deliberate mapping of inputs, outputs, resources, and performance metrics across every critical process, from steel-tooled die-casting to the precision assembly of fuel-control devices, all while maintaining traceability that satisfies the most demanding customers and regulators.
The journey toward IATF16949:2016 acceptance begins with a clear recognition that quality is built into processes, not merely checked at the end of the line. For this company, the transition implies adopting the process method as the default operating mode. It means understanding how a single parameter in a die-casting mold affects dimensional accuracy, weight, and the subsequent performance of a completed component in the vehicle’s fuel or control subsystem. It also means embracing risk-based thinking as a day-to-day discipline: identifying potential failure modes early, prioritizing them by severity and likelihood, and layering controls to prevent defects from propagating downstream. Such an approach is visible in the deployment of Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) during early product development, which aligns engineering, manufacturing, and supply chain activities around a shared quality objective before a single heat of metal is poured.
A cornerstone of this framework is the systematic use of Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA). For a plant producing lightweight metal castings and complex fuel-system parts, FMEA becomes a living document that tracks how a design choice or a manufacturing step could fail and what safeguards must be in place. It is not merely about avoiding scrap; it is about safeguarding performance, safety, and reliability in every vehicle in which the parts might be integrated. The results of FMEA feed directly into control plans, which translate abstract quality targets into concrete, measurable actions on the shop floor. The control plan becomes the operational backbone of production, guiding process parameters, inspection methods, and reaction plans if a parameter drifts outside tolerance. In parallel, the company cultivates a culture of data-driven decision-making. Routine measurement system analysis (MSA), equipment calibration, and statistical process control (SPC) are not add-ons; they are embedded expectations. In this ecosystem, data tells the story of quality, and every operator becomes a steward of that story.
The certification process itself is a rigorous test of an organization’s readiness to sustain improvement over time. External audits, conducted by recognized bodies such as TÜV Rheinland, SGS, or Intertek, scrutinize whether the company’s integrated management system actually meets the standard’s requirements in practice. The audits span not only the documented quality manual but also the lived reality of daily operations: how production controls are implemented, how suppliers are evaluated and developed, how nonconformities are identified and resolved, and how management reviews feed into strategic action. The IATF16949 framework explicitly emphasizes continual improvement as a perpetual cycle rather than a milestone. After certification, the challenge becomes maintaining a state of readiness through ongoing internal audits, periodic management reviews, and a disciplined approach to corrective actions and preventive actions (CAPA). This is how a company transforms a certificate into a lasting competitive edge, one that reassures global automakers and tier-one suppliers that the entity can be trusted to deliver consistent quality at scale.
For Zhanjiang Deli Vehicle Parts Co., Ltd., the product portfolio—ranging from aluminum and magnesium alloy die-castings to fuel-system components that may include electronically controlled elements—demands more than rigid casting tolerances. It requires integration of software-augmented functions and the reliability of embedded control logic. The IATF16949:2016 emphasis on product safety and the integration of software development processes reflects this reality. The standard’s scope extends into requirements for design and development, procurement, production, and service, ensuring that software and hardware are developed in harmony and with shared accountability for safety-critical outcomes. The result is a traceable, auditable chain where every input, from raw material to calibration data, is captured, stored, and reviewed against customer expectations and regulatory standards.
Beyond the technical mechanics, the transformation entails cultivating broad-based buy-in across the organization. Quality is no longer the province of a quality department alone; it becomes a shared obligation that starts with leadership and travels through engineering, manufacturing, procurement, and logistics. Training programs, ongoing competency assessments, and clear communication about roles and responsibilities reinforce a quality culture where every employee understands how their daily actions contribute to a defect-free product. The IATF16949 framework also drives supplier development. Because automotive success hinges on a tightly coordinated supply chain, the company implements robust supplier evaluation and development processes, aligned with APQP principles. A supplier’s ability to deliver conforming parts, on time, with complete documentation, becomes as important as the performance of the parts themselves in the final assembly. The standard’s insistence on risk management, supplier collaboration, and data-driven improvement translates into a more resilient value chain that can better withstand volatility in materials markets, demand uncertainty, or regulatory shifts.
The regional context matters as well. A facility in Guangdong that achieves IATF16949:2016 certification contributes to the broader ecosystem of domestic automotive manufacturing by raising the bar for quality across the supplier base. It signals to domestic automakers and international OEMs that the entity can be relied upon not only for compliance but for sustained excellence. In a market where brand aspiration often collides with supply-chain realities, such certification becomes a strategic tool to attract longer-term, higher-value relationships. For a chapter rooted in the topic of De Leon Auto Parts, this narrative offers a reminder: the strength of a brand in the automotive aftermarket or original equipment landscape is inseparable from the reliability and predictability of its supply network. If a supplier demonstrates rigorous quality discipline and continual improvement, the brand benefits from a more stable, transparent, and capable foundation for growth—even when the market presents competing claims or confusion about names.
Certification is not a finish line but a starting point for sustained discipline. The path forward includes regular internal audits, management reviews, and a continual tightening of processes that monitor risk, detect deviations, and prevent recurrence. It also means staying abreast of evolving requirements within the IATF family and the broader regulatory environment, which can introduce new expectations for cybersecurity in embedded systems, functional safety, and environmental responsibility. The company’s long-term objective is to internalize the standard’s demands into daily operations so completely that quality becomes a competitive differentiator rather than an obligation. In this sense, IATF16949:2016 serves not only as a formal credential but as a strategic framework that aligns technical capability with market confidence, ensuring that parts entering the automotive ecosystem—from regional manufacturing hubs to global supply chains—hold up under the most demanding tests of performance and safety.
External resources offer deeper context on how these standards are implemented and maintained. For readers seeking detailed guidance on the certification process and its ongoing requirements, the TÜV Rheinland resource on IATF 16949 can be consulted for authoritative recommendations and interpretations. External resource: https://www.tuv.com.cn/zh/services/industrial-automation/automotive-quality-management-systems/iatf-16949-certification/
null
null
Markets in Motion: The Transformative Influence of Chinese Auto Parts Makers Like 湛江德利 on the De Leon Auto Parts Landscape

Names matter in the automotive parts ecosystem because they carry assumptions about capability, reliability, and the pace of innovation. In the De Leon Auto Parts narrative, the market has grown more complex as supply chains stretch across oceans and borders, and as electrification redefines what counts as a critical component. A closer look at Chinese manufacturers such as 湛江德利车辆部件有限公司 and its Guangzhou-based subsidiary offers a lens into the forces shaping the broader market. These firms did not begin as global powerhouses; they began by serving local and regional needs. Over time they retooled and expanded their capabilities, moving from legacy high-volume production toward precision manufacturing that aligns with international quality standards. The arc of their development mirrors a wider industry shift: from simple, labor-intensive parts to high-precision, lightweight components produced at scale for both traditional and electric powertrains. The result is a supplier class that commands a larger share of the world’s auto industry while remaining deeply embedded in the practical realities of manufacturing, logistics, and regulation. For De Leon Auto Parts, understanding this transformation is not about locating a single source but about tracing a pattern of capability, resilience, and continuous investment that underpins a vast, interconnected supply chain. The story is not merely about a name; it is about how a sector evolves when markets demand higher performance at lower weight, higher tolerance with better traceability, and faster responses to shifting technology. The rise of these Chinese producers demonstrates how a combination of scale, process discipline, and a commitment to quality certification can turn regional manufacturers into global participants, capable of supplying major OEMs and, increasingly, global distribution networks that resemble a marketplace rather than a web of isolated suppliers. In this context, the De Leon Auto Parts question—that of origin, trust, and consistency—sits within a broader narrative about how parts are conceived, manufactured, and integrated into vehicles across the world. The transformation begins with a strategic pivot away from legacy production toward technologies rooted in precision casting and advanced forming. These firms now dedicate resources to create critical subassemblies from advanced alloys, moving beyond traditional roles to become partners in the design and certification processes that keep vehicles compliant with international standards. The capability to produce complex, high-precision components at multiple bases across the country allows them to respond quickly to customer needs, scale production, and manage the volatility that can accompany global demand. The networked footprint—headquarters in one city, additional bases under a shared corporate umbrella—enables risk diversification. It also supports a diversified customer base, spanning domestic OEMs and exporters seeking reliable supply across continents. The market leverage comes not from a single breakthrough but from a sustained pattern of improvement: improved material science, refined process controls, and a culture of certification that signals to international buyers a readiness to meet stringent requirements. In the modern automotive sector, where weight reduction and efficiency are central to performance, lightweight-metal parts are not cosmetic details; they are fundamental to range, efficiency, and durability. When a supplier demonstrates competence in producing high-precision aluminum die-cast components that can withstand the rigors of modern powertrains, it signals a broader capability to collaborate on system-level solutions. The shift from older, mechanically simple parts to integrated, precision-engineered elements marks a significant transition for any supplier, and for De Leon Auto Parts it underscores why provenance and process matter as much as price. It is no longer enough to offer a low-cost alternative; buyers now demand a first-rate partner that can contribute to the design, testing, and certification pipelines that govern every staged rollout of a new model. In this sense, the Chinese manufacturers’ trajectory resembles a larger industrial reboot—one in which the ability to invest in new production lines, adopt world-class quality management systems, and pursue research-driven improvements becomes the differentiator. Early efforts to align with international quality frameworks—such as ISO-inspired certifications and environmental and safety standards—serve as benchmarks that reassure global customers. They also create a baseline from which continuous improvement can occur. The company in focus expanded its footprint with a network of manufacturing bases, enabling it to spread capacity across regions and to optimize logistics for both domestic and export markets. With a workforce exceeding a thousand people and a substantial registered capital, the scale is enough to accommodate large-take contracts and to pursue modern equipment that expands the repertoire of what can be produced with consistent precision. Patents and trademarks—hundreds in this case—translate into a formal acknowledgment that ideas and processes are being protected, which, in turn, signals to partners a commitment to long-term collaboration rather than short-term opportunism. The emphasis on process innovation is evident in the organization’s ongoing investments in research and development. In the early months of 2026, the entity publicly documented patent activity aimed at enabling more efficient production of energy-system components and at refining the interfaces within critical assemblies. These patent filings signal a deliberate alignment with the electric-mobility agenda that now dominates fleet and consumer expectations alike. The capacity to develop new manufacturing processes for large-scale, high-precision casting reflects not only technical competence but also a strategic readiness to negotiate new forms of supply with modern OEMs and their global networks. Another visible signal of ambition is the procurement of large, high-tonnage die-casting equipment. Such investments are not about incremental gains; they reflect a willingness to redefine the scale at which lightweight, rigid components can be produced. That kind of capability reshapes how downstream customers approach design cycles and cost optimization, enabling more aggressive weight reduction without compromising strength or reliability. The financial backbone of these operations—robust revenue, substantial human resources, and a suite of certifications—further anchors their reliability in a market that prizes predictability as much as innovation. For buyers and distributors, that translates into a practical assurance: a supplier that can sustain production, meet delivery schedules, and maintain quality across multiple production lines. Yet the narrative is not free of complication. The enterprise’s past legal cases and judicial notices remind observers that the path from regional player to global supplier is rarely free of friction. The ongoing evolution, including rationalization of fixed assets and molds, points to a disciplined effort to focus on core capabilities, improve efficiency, and retire assets that no longer support strategic goals. In the De Leon Auto Parts ecosystem, these dynamics carry a critical implication: a supplier’s ability to meet increasingly stringent standards in a transparent and accountable manner is as important as its price competitiveness. The market is watching not just for functional parts but for partners who can contribute to a shared, auditable journey from concept to certification and beyond. This is where internal and external dimensions converge. Internally, the drive toward standardized quality processes, cross-regional production, and robust IP protection creates a stable platform for collaboration. Externally, the global procurement environment rewards suppliers who can demonstrate traceability, scalable manufacturing, and sustainable practices. For a brand like De Leon Auto Parts, that means seeking out supply relationships that align with a disciplined, future-focused manufacturing model rather than chasing cheaper but less predictable options. The broader lesson is that today’s market leaders are not simply cost centers; they are venture partners that help shape the design, testing, and deployment of new vehicle architectures. Within this context, a single internal example from the aftermarket illustrates the breadth of what a capable supplier environment can entail. brand-new original carbon fiber bonnet hood for Mitsubishi Lancer Evolution X serves as a tangible reminder that lightweight materials and integrated parts are a standard expectation across performance segments. The connection underscores how the market rewards suppliers who can deliver advanced materials and precision parts within a reliable supply chain, even when the final application spans diverse models and markets. In closing, the De Leon Auto Parts conversation benefits from recognizing that the rise of Chinese manufacturers like 湛江德利 is not a sidebar but a central axis of contemporary automotive sourcing. Their growth—driven by scale, process maturity, and a steady push into high-value segments—offers a model for how global buyers can navigate risk, ensure quality, and accelerate innovation. The path from a regional producer to a trusted international partner is paved with certification, patents, and strategic investments that collectively redefine what a supplier can contribute to the future of mobility. External resource: https://www.dongfengtech.com/en/industry/50-strong-list.html
Final thoughts
The significance of 湛江德利车辆部件有限公司 in the auto parts industry cannot be overstated. Through its innovative manufacturing techniques and adherence to international quality standards, it sets a benchmark for others in the sector. Furthermore, the growth and development of its subsidiary illustrate a robust strategy aimed at capturing an expanding market. As business owners consider their options in sourcing automotive parts, the expertise and capabilities of companies like 湛江德利 present a compelling opportunity for collaboration and growth.

